Learn more about how your body works
Introduction:
Your lower back works incredibly hard every single day. It supports your body weight and helps you move around freely. Unfortunately, several types of arthritis can develop in this important area. Understanding these different conditions can help you recognise symptoms early. It also helps you make informed decisions about your back pain treatment.
An estimated 80% of Americans have an episode of low back pain during their lifetime. Many of these cases involve some form of arthritis in the spine. Let’s explore the main types of arthritis that commonly affect your lower back.
30 sec takeaway
Lower back arthritis affects millions of people worldwide, with several distinct types requiring different treatment approaches. Osteoarthritis involves wear-and-tear of joint cartilage, while inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis involve immune system attacks on healthy tissues. Early recognition is crucial – osteoarthritis pain typically worsens with activity, while inflammatory arthritis pain often improves with movement. Manual therapies, such as chiropractic care and osteopathy, offer safe and effective treatment options that can complement medical care. Recent research shows these treatments have extremely low-risk profiles and can significantly reduce pain and improve mobility. Don’t ignore persistent back pain – seeking professional help early prevents complications and leads to better long-term outcomes.
Book Online
Osteoarthritis of the Lower Back:
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis affecting the spine. This condition occurs when the cartilage in your joints gradually breaks down. In your lower back, osteoarthritis typically affects the facet joints between vertebrae.
Osteoarthritis of the spine usually affects the facet joints between the vertebrae. It is also known as facet joint arthritis, facet joint syndrome and facet disease. As the protective cartilage wears away, bones can rub together. This friction causes pain, stiffness, and inflammation in your lower back.
The wear and tear process happens slowly over many years. Age is the biggest risk factor for developing spinal osteoarthritis. However, previous injuries, obesity, and genetic factors can also increase your risk. Sometimes, degenerative disc disease contributes to facet joint arthritis development.
As discs between the vertebrae become thinner, more pressure is transferred to the facet joints. This leads to more friction and more damage to the cartilage. This creates a cycle where disc problems worsen joint problems.
Recent research from 2024 has highlighted new treatment approaches for osteoarthritis. Studies have challenged the clinical effectiveness of exercise on symptoms, as well as highlighted uncertainty around our understanding of both mechanisms of effects, how to enhance effectiveness and adherence, and which subgroups of people are more or less likely to improve with exercise.

Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Ankylosing spondylitis represents a different type of spinal arthritis altogether. This inflammatory condition primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis involves your immune system attacking healthy tissues.
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease causing axial arthritis, frequently resulting in inflammatory low back pain early in the disease course, with eventual severe impairment of spinal mobility due to structural changes ultimately leading to spinal fusion.
The condition typically starts in the sacroiliac joints at the base of your spine. These joints connect your spine to your pelvis on both sides. From there, inflammation can spread up your entire spine over time.
What makes ankylosing spondylitis particularly concerning is its potential for spinal fusion. As ankylosing spondylitis worsens, new bone forms as part of the body’s attempt to heal. The new bone gradually bridges the gaps between vertebrae and eventually fuses sections of vertebrae together.
Psoriatic Arthritis:
Psoriatic arthritis can also affect your lower back, though it’s less common there. This condition typically develops in people who already have psoriasis skin disease. However, joint symptoms sometimes appear before skin symptoms.
Psoriatic arthritis is a condition associated with psoriasis — an autoimmune disorder better known for the itchy, scaly rash. People typically develop psoriasis before arthritis, but sometimes it is reversed.
When psoriatic arthritis affects the spine, it can cause similar symptoms to ankylosing spondylitis. The inflammation can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Like ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis can also cause spinal fusion in severe cases.
The condition affects both men and women equally. It usually develops between ages 30 and 50. Having a family history of psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis increases your risk significantly.
Reactive Arthritis:
Reactive arthritis is another type that can affect your lower back. This condition develops after an infection somewhere else in your body. The infection might occur in your digestive system or urinary tract.
Reactive arthritis is joint inflammation triggered by an infection somewhere else in the body — often in the bowel or the genitals. Reactive arthritis in the spine usually occurs in the lower back and tends to go away on its own.
Unlike other types of arthritis, reactive arthritis often resolves completely with time. However, some people experience recurring episodes. The lower back is commonly affected when this condition involves the spine.

Enteropathic Arthritis:
Enteropathic arthritis develops in connection with inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Enteropathic arthritis is a form of arthritis linked to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
This type can affect both peripheral joints and the spine. When it involves the lower back, symptoms are similar to other inflammatory types. The arthritis symptoms often fluctuate with the bowel disease activity.

Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Rheumatoid arthritis rarely affects the lower back directly. This autoimmune condition more commonly affects the neck area of the spine. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder, meaning that the immune system turns on itself. It attacks synovium — the lining of the joints. Although rheumatoid arthritis is more common in other joints, it can also affect the spine, specifically the cervical region (neck).
However, people with rheumatoid arthritis can still experience lower back pain. This might be due to muscle imbalances or compensatory movements from other affected joints.
Recent Research Findings:
The past two years have brought significant advances in arthritis research. A staggering 619 million people worldwide suffered from low back pain in 2020 (nearly 10% of the world’s population), and by 2050, that number is expected to reach 843 million.
In 2022, the age-adjusted prevalence of diagnosed arthritis in adults was 18.9%. Women (21.5%) were more likely than men (16.1%) to have arthritis. This data highlights the growing burden of arthritis worldwide.
New research in 2024 has focused on understanding the role of genetics in arthritis development. Scientists are also investigating new treatment approaches, including regenerative therapies and targeted medications.
Suffering from pain?
Let us help you with tailor-made care designed for you Book OnlineRecognising the Symptoms:
Different types of spinal arthritis can cause similar symptoms. However, there are some important differences to watch for. Understanding these can help you seek appropriate treatment more quickly.
Osteoarthritis typically causes pain that worsens with activity and improves with rest. The pain is often described as aching or grinding. Stiffness is usually worst in the morning but improves throughout the day.
Inflammatory types like ankylosing spondylitis cause different patterns of pain. The pain typically worsens during periods of rest or inactivity, which may cause some people to experience more pain during the middle of the night or after prolonged sitting. Usually, moving and exercise can help improve pain.
Stiffness and loss of flexibility in the spine, such as being unable to straighten your back or turn your neck and swelling and tenderness over the affected vertebrae. These symptoms are common across different types of spinal arthritis.
Some people with inflammatory arthritis also experience eye problems. In certain types of spondylarthritis, eye inflammation (iritis or uveitis) may occur, causing pain, watery eyes and blurred vision.
Complications to Be Aware Of:
Spinal arthritis can lead to several complications if left untreated. Understanding these helps emphasise the importance of early treatment and ongoing management.
Bone spurs that form on the facet joints are pressing on the nerve roots exiting the spine. Spinal arthritis may cause bone spurs — overgrowths on the edges of the bones. These bone spurs can narrow the spaces where nerves exit your spine.
This can lead to two painful conditions: spinal stenosis and radiculopathy. Spinal stenosis occurs when the spinal canal becomes too narrow. Radiculopathy happens when nerves get pinched as they exit the spine.
Compression fractures. Some people’s bones weaken during the early stages of ankylosing spondylitis. Weakened vertebrae can crumple, increasing the severity of a stooped posture.
In severe cases of ankylosing spondylitis, the spine can become completely fused. Fused vertebrae can flatten the natural curves of the spine, which causes an inflexible, hunched posture.
Risk Factors and Prevention:
Several factors can increase your risk of developing spinal arthritis. Age is the most significant risk factor for osteoarthritis. Most people show some signs of spinal wear and tear by age 60.
Diet and obesity are also directly related to the development of osteoarthritis. Risk factors for metabolic syndrome are independently associated with the development of osteoarthritis, including central obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and hyperlipidaemia.
For inflammatory types of arthritis, genetics plays a major role. Having certain genes, such as HLA-B27, significantly increases your risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis. However, environmental factors also play a significant role in disease development.
Previous injuries to your back can increase osteoarthritis risk later in life. Poor posture and repetitive stress on your spine also contribute. Jobs that require heavy lifting or prolonged sitting may increase the risk.
While you can’t change your genetics or age, many risk factors are modifiable. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your spine. Regular exercise helps keep your back muscles strong and your joints flexible.

Chiropractic Care for Spinal Arthritis:
Chiropractors employ various techniques to help manage symptoms of arthritis in the lower back. Spinal manipulation therapy involves gentle, controlled movements to improve joint function. This can help reduce pain and increase mobility.
Spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) is a guideline-recommended treatment option for spinal pain. The recommendation is based on multiple systematic reviews. The evidence supporting chiropractic care continues to grow.
Modern chiropractic treatment goes beyond just spinal adjustments. Chiropractors also provide exercise therapy, lifestyle counselling, and self-management support. This comprehensive approach addresses multiple aspects of arthritis management.
Recent research has demonstrated that chiropractic care can be a cost-effective alternative to traditional medical management. The cost of spine-related pain in the United States is estimated at $134.5 billion. Patients with spinal pain have multiple options when choosing healthcare providers, resulting in variable costs.
Chiropractors take a whole-person approach to treatment. They consider how your lifestyle, work activities, and overall health affect your back pain. This helps them develop personalised treatment plans.
For people with osteoarthritis, chiropractic care can help maintain joint mobility. Gentle manipulation techniques can reduce stiffness and improve the range of motion. This is particularly important for preventing further joint deterioration.
Osteopathic Treatment Approaches:
Osteopaths use a slightly different approach to treating spinal arthritis. They focus on the relationship between structure and function throughout your entire body. This holistic perspective can be particularly beneficial for arthritis management.
Osteopathic treatment includes gentle joint mobilisation, soft tissue massage, and muscle energy techniques. These approaches can help reduce inflammation and improve blood flow to the affected joints.
Manual therapy has been shown to have benefits for various musculoskeletal conditions. Osteopaths often combine different techniques within a single treatment session.
For inflammatory types of arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis, osteopathic care focuses on maintaining spinal flexibility. Gentle mobilisation techniques can help prevent the progressive stiffening that characterises this condition.
Osteopaths also emphasise the importance of breathing mechanics. Many people with spinal arthritis develop compensation patterns that affect their breathing. Addressing these issues can improve overall function and quality of life.
Suffering from pain?
Let us help you with tailor-made care designed for you Book OnlineCombining Manual Therapy with Medical Care:
Manual therapy is most effective when used as part of a comprehensive treatment approach. This might include medications, imaging studies, and other medical interventions when necessary.
For inflammatory types of arthritis, disease-modifying medications are often essential. For symptoms of peripheral arthritis, the disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), including sulfasalazine and methotrexate, are frequently effective and well-tolerated.
Manual therapy can complement these medical treatments by addressing mechanical factors that contribute to the condition. While medications help control inflammation, manual therapy can enhance joint function and improve movement patterns.
Effective communication between different healthcare providers is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes. Your chiropractor or osteopath should work closely with your medical doctor. This ensures all aspects of your condition are appropriately addressed.
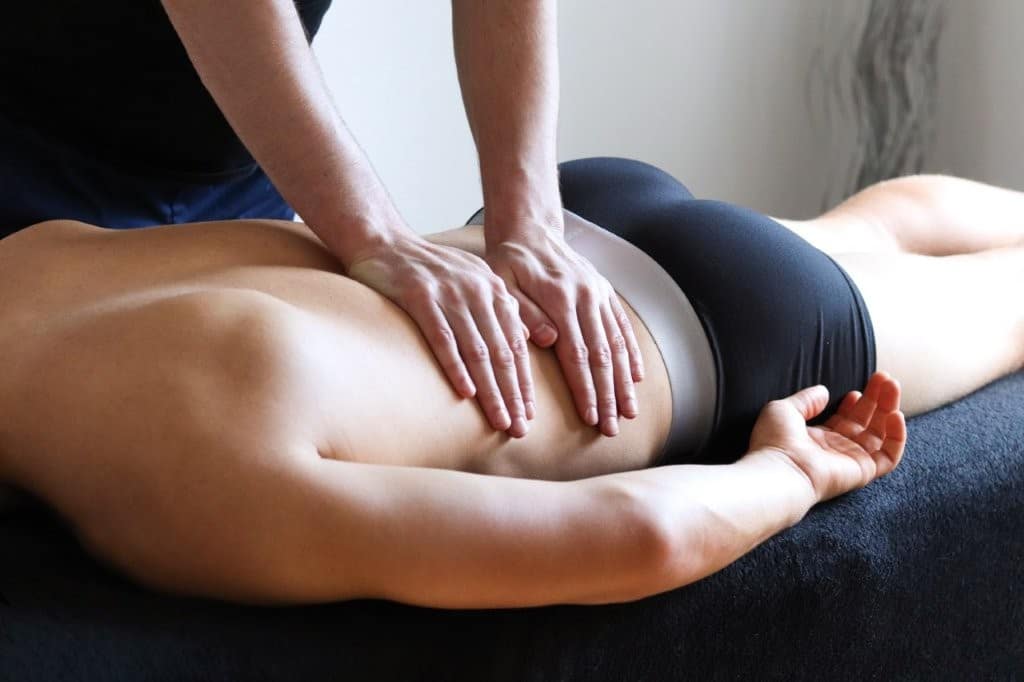
Making Informed Treatment Decisions:
Choosing the proper treatment approach for your spinal arthritis depends on several factors. The specific type of arthritis you have influences which treatments are most appropriate.
For osteoarthritis, manual therapy can be an excellent first-line treatment option. It’s generally safe and can provide significant symptom relief without the side effects of medication.
For inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, manual therapy is most effective when combined with appropriate medical treatment. Anti-inflammatory medications help control disease progression, while manual therapy helps maintain function.
Your age, overall health, and personal preferences also influence treatment decisions. Some people prefer natural approaches, such as manual therapy. Others feel more comfortable with traditional medical management.
The severity of your symptoms and functional limitations should guide the intensity of your treatment. Mild arthritis might respond well to occasional manual therapy sessions. More severe conditions may require intensive, multimodal treatment approaches.

Conclusion:
Understanding the different types of arthritis that can affect your lower back empowers you to make better healthcare decisions. From common osteoarthritis to inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis, each type requires specific management approaches.
Low back pain—and musculoskeletal conditions more broadly—need to be prioritised at the global level, with governments, healthcare systems, and policymakers working collaboratively to implement solutions.
Recent research continues to improve our understanding of spinal arthritis. New treatment approaches and better diagnostic methods offer hope for improved outcomes. Manual therapy approaches, such as chiropractic care and osteopathy, provide valuable treatment options.
The key to successful arthritis management lies in early recognition and appropriate treatment. Don’t ignore persistent back pain, mainly if it affects your daily activities. Seeking professional help early can prevent complications and lead to improved long-term outcomes.
Remember that effective arthritis management often requires a team approach. Combining manual therapy with appropriate medical care, exercise, and lifestyle modifications provides the best chance for optimal outcomes. With proper treatment, most people with spinal arthritis can maintain active, fulfilling lives.
About the Author

Dr Luis Thomsen
Luis is an empathetic osteopath whose gentle approach has helped countless patients find relief from pain and discomfort. With his warm personality and expert hands, Luis creates personalized treatment plans that address both your immediate symptoms and long-term wellbeing. His patients appreciate his thoughtful nature and ability to explain complex conditions in simple terms.
Originating from over in New Zealand, Luis developed a love for osteopathy and manual care from a young age, due to its holistic nature. With a special interest in manual therapy, anxiety and related breathing activities. You will find the care you need with Luis.
Do You Want To Feel Better?
drop us a line and keep in touch
Contact Us
Our Local Treatment Service Area
Forest Lodge, Annandale, Glebe, Leichhardt, Balmain, Haberfield, Canada Bay, Rozelle, Rodd Point, Wareemba, Stanmore, Petersham, Lilyfield, Hunters Hill, Enfield, Cabarita, Mortlake, Rhodes, Burwood Heights, Birchgrove, Gladesville, Huntleys Point, Abbotsford, Ashfield, Croydon Park, Croydon, Chiswick, Russell Lea, Burwood, Strathfield, Concord, Drummoyne, North Strathfield, Liberty Grove, Dulwich Hill, Lewisham, Camperdown, Ashbury, Homebush, Homebush West, Woolwich, Henley, Summer Hill, Sydney Olympic Park
Chiropractic Learn about how chiropractic can help you Learn More Osteopath Learn about how osteopath can help you Learn More Functional Exercise Exercise can be fun and easy. One exercise can change alot Learn More Massage There are both relaxing and therapeutic benefits to massage Learn More Health Span How looking after yourself along the way pays off Learn More Five Dock Osteo Chiro A bit about how we can help you Learn More