- 02 9712 1736
- [email protected]
- 212 Great North Road, Five Dock, NSW 2046
- Open 7 days a week
Tendonitis is the medical term used to describe inflammation of tendons – tough, fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones. Tendonitis is commonly caused by overuse or injury and can affect tendons in any part of the body. In this post, we will cover what tendonitis is, common tendons that are affected by tendonitis, its symptoms, causes, and how it can be treated.
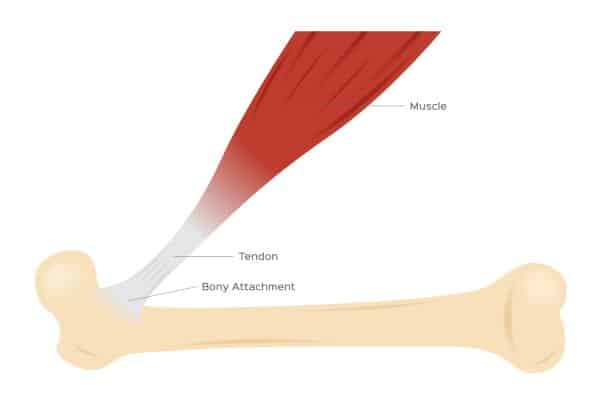
Tendons are strong bands of tissue that join muscles to bones. Healthy tendons are both strong and flexible. They are strong enough to withstand the stress of repeated muscle contraction but also flexible enough to transfer the force of muscle contractions to your bones to allow for movement. Within your tendons are collagen fibres arranged in parallel bundles, which give tendons their tensile strength. When tendons become inflamed, swelling leads to reduced flexibility affecting your range of movement, and you end up with significant pain with movement.
Inflammation of your tendon, or tendonitis, occurs as a result of overuse or an acute injury. This condition can occur in any of the tendons throughout your body, leading to inflammation, pain, and discomfort in the affected area. Tendonitis is common among athletes, manual laborers, and even people engaged in repetitive tasks like typing. Unlike arthritis, which affects the joints, tendonitis specifically targets the tendons, causing localised inflammation and pain.
Pain associated with the condition tends to be localised to where the affected tendon joins to a bone. Movement involving the affected tendon intensifies the pain significantly. Mild swelling is another common symptom. This is often accompanied by tenderness to touch.
In addition to pain and swelling, many individuals with tendonitis experience a reduced range of motion in the affected area. This limitation is due to the inflammation and pain that make it difficult to move the tendon freely. Early recognition of these symptoms allows for timely treatment, reducing the risk of further complications.
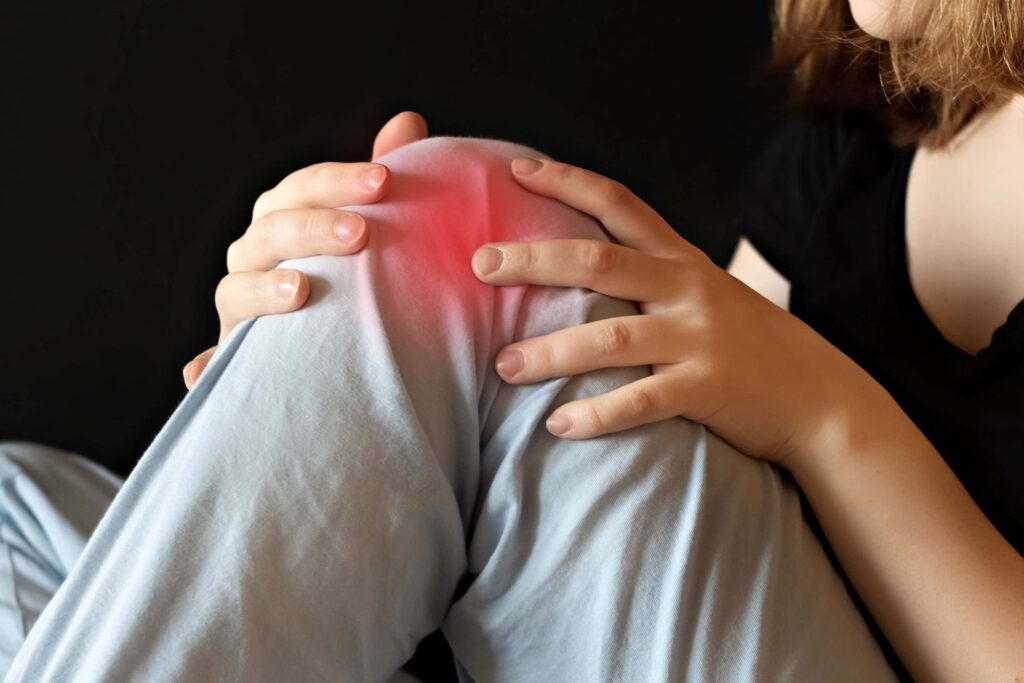
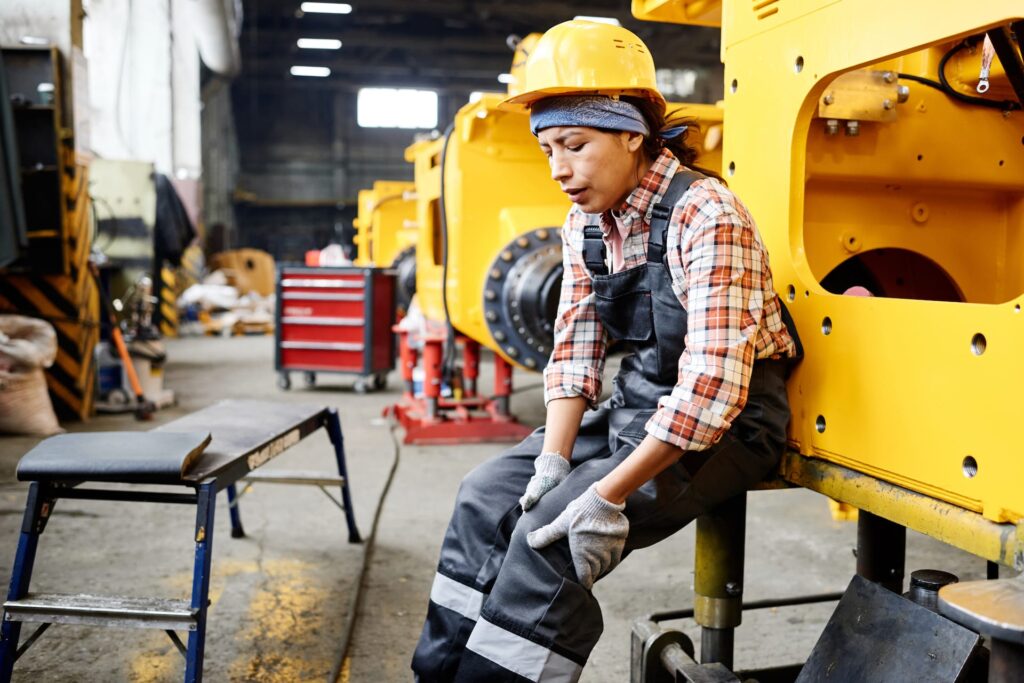


Excessive stress on tendons leads to tendonitis. Excessive stress could be a result of repetitive physical tasks involving the tendon, engaging in activities with improper movement patterns leading to unnatural loading of the tendon, or an acute injury involving trauma to the tendon.
Specific activities are known to contribute to different types of tendonitis. We will explore this in the next section where we take a look at common tendons that often become affected by this condition. Modifying routines and adopting better practices can help avoid developing tendonitis.
Tendonitis are named differently based on the affected area and the specific tendons involved. Some of these have unique characteristics, causes, and symptoms, depending on the location of the tendonitis.
1. Achilles Tendonitis
Achilles tendon inflammation is often due to excessive walking, running, or jumping activities that put excessive stress on the Achilles tendon.
2. Patellar Tendonitis (Jumper’s Knee)
Patellar tendon inflammation is often due to repetitive jumping and landing that put excessive stress on the patellar tendon.

3. Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Rotator cuff tendon inflammation is often due to repetitive overhead movements that put excessive stress on the rotator cuff tendons.
4. Biceps Tendonitis
Biceps tendon inflammation is often caused by repetitive lifting or overhead activities that put excessive stress on the biceps tendon.
5. Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Common extensor tendon inflammation is often due to repetitive stress and overuse, particularly in activities that require elbow flexion, that put excessive stress on the common extensor tendon.
6. Golfers Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
Common flexor tendon inflammation is often due to repetitive stress and overuse of the wrist and fingers that put excessive stress on the common flexor tendon.
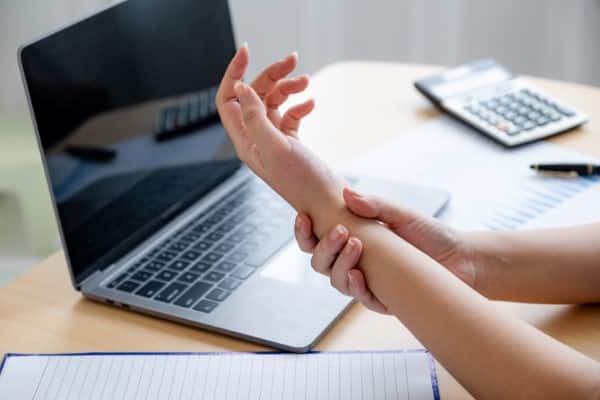


7. Wrist Tendonitis
Wrist tendons inflammation is often due to repetitive strain from repetitive tasks like typing that put excessive stress on wrist tendons.
8. De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Inflammation of the tendon sheath of the thumb is often due to repetitive thumb and wrist movements that put excessive stress on the tendon sheath.
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing tendonitis. Age is a significant factor. Tendons naturally lose flexibility over time, making them more susceptible to injury. Certain physical occupations that involve repeated motions or awkward positions, such as manual labour, also heighten the risk of tendonitis.
Medical conditions like diabetes can elevate the likelihood of experiencing tendonitis. Additionally, sudden increases in physical activity intensity or engaging in activities without proper form can contribute to the development of tendon problems.
Some medications, including specific antibiotics and corticosteroids, can increase the risk of tendon injuries.
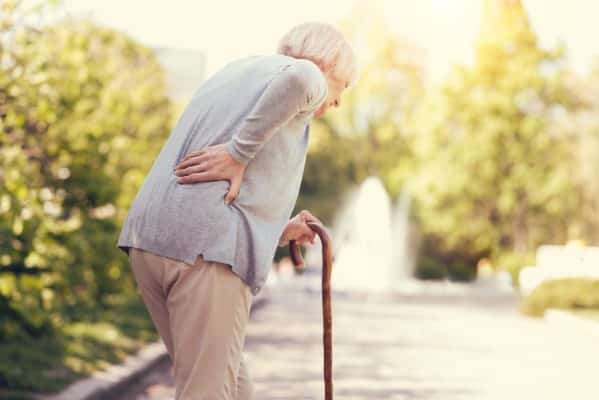

Diagnosing tendonitis typically involves a combination of a thorough patient history and physical examination. Understanding how the pain started, the location and characteristics of the pain, and the types of movements that affect the pain provides your health practitioner with the information they need to make a diagnosis. Imaging techniques such as ultrasound and MRI can be used to visualize tendon abnormalities and confirm the diagnosis of tendonitis. These imaging tests are particularly effective in identifying the severity and extent of tendon injuries associated with tendonitis.
Conservative or non-surgical care is usually effective and recommended as a a starting point. Care is aimed at reducing pain and inflammation. Here is a breakdown of what the typical conservative approach entails.
Resting the affected tendon and avoiding the specific activity that caused tendonitis are crucial steps to allow the tendon to heal. Using a bandage, splint, or brace can help reduce movement of the affected tendon, aiding in the healing process.
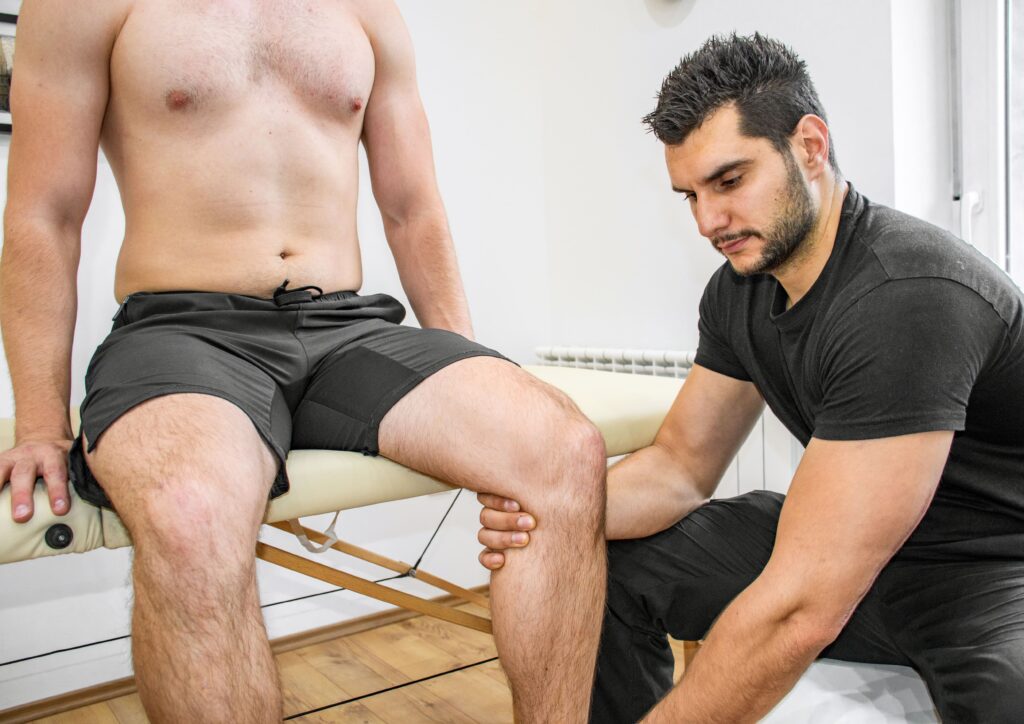


Manual therapy techniques, involving targeted soft tissue work, can help with recovery. Joint mobilisation can also be beneficial to improve quality of movement of the affected joints. Specific exercises can be introduced to strengthen surrounding muscles and rehabilitate the tendons. Combining targeted rehabilitation exercises with manual therapy techniques offers a comprehensive approach to effectively treating tendonitis.
Managing pain and inflammation using over-the-counter NSAIDS can be helpful to enhance recovery and restore function. Over-the-counter NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are commonly recommended to help reduce pain and inflammation so that manual therapy and rehabilitative exercises can be done.
For persistent pain and inflammation, corticosteroid injections can effectively alleviate symptoms by delivering medication directly to the inflamed tendon. This method provides significant relief but may be temporary if the aggravating activity and underlying injury is not addressed properly.
Surgery may be necessary for severe cases of tendonitis, particularly when other treatments have failed. The surgical procedures aim to realign tendons, remove bone spurs, and address calcium buildup, depending on the location of the affected tendon.
Preventing tendonitis is vital for long-term joint health and functionality. Exercises tailored by a physical therapist can enhance muscle strength and tendon resilience, reducing the risk of overuse injuries. Stretching and strengthening muscles exercises for the wrists and forearms can also improve flexibility and muscle strength.
Proper ergonomics, such as using tools with neutral wrist positions and taking regular breaks during repetitive tasks, can help minimize tendon strain. By adopting these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing tendonitis and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.

Understanding tendonitis, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential in managing and preventing this painful condition. By recognizing the early signs of tendonitis and seeking appropriate treatment, you can reduce pain and inflammation, promoting healing and preventing chronic issues.
Taking proactive measures to prevent tendonitis, such as engaging in proper physical activities, using ergonomic tools, and performing targeted exercises, can ensure long-term joint health and functionality. Remember, maintaining a balance between activity and rest is key to keeping your tendons healthy and strong.
Forest Lodge, Annandale, Glebe, Leichhardt, Balmain, Haberfield, Canada Bay, Rozelle, Rodd Point, Wareemba, Stanmore, Petersham, Lilyfield, Hunters Hill, Enfield, Cabarita, Mortlake, Rhodes, Burwood Heights, Birchgrove, Gladesville, Huntleys Point, Abbotsford, Ashfield, Croydon Park, Croydon, Chiswick, Russell Lea, Burwood, Strathfield, Concord, Drummoyne, North Strathfield, Liberty Grove, Dulwich Hill, Lewisham, Camperdown, Ashbury, Homebush, Homebush West, Woolwich, Henley, Summer Hill, Sydney Olympic Park

About
Five Dock Osteopathic & Chiropractic is located in Canada Bay, in Sydney’s Inner West. Servicing suburbs including Burwood, Croydon, Drummoyne, Five Dock, Haberfield, Concord, Abbotsford, Chiswick, Leichhardt, Wareemba, Russell Lea, Summer Hill, Strathfield.
Clinic hours
Monday, Tuesday, Thursday 7AM – 7PM
Wednesday, Friday 7AM – 6PM
Saturday 7AM – 2PM
Sunday 8AM – 2PM
Contact details