- 02 9712 1736
- [email protected]
- 212 Great North Road, Five Dock, NSW 2046
- Open 7 days a week
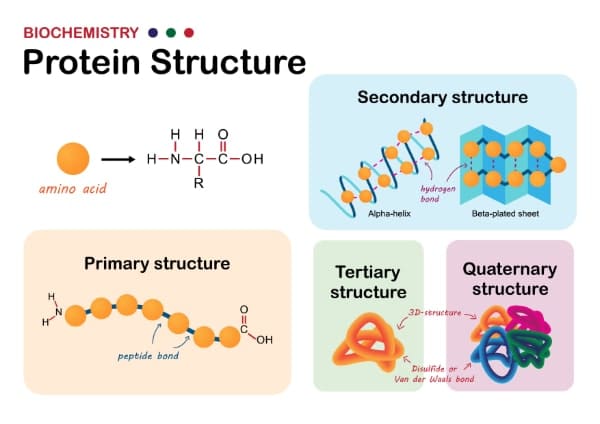
Proteins serve as one of many essential building blocks of life. As such, ensuring adequate protein volume in the body is highly important. Proteins are necessary to allow our bodies to maintain both structure and function. Proteins are mostly associated with muscle growth. But did you know? They are necessary for various bodily functions, such as the immune system and hormonal regulation to work. A common misconception is that only bodybuilders aiming to bulk up would be concerned with their protein intake. In reality, maintaining an adequate level of protein intake is relevant to every one of us. A number of factors including age and activity level influence the recommended amount of protein intake that each person requires. In this post, we will discuss the significance of protein intake, explore the diverse bodily functions that rely on proteins, and delve into dietary requirements to maintain a healthy and active body.
Proteins are large complex molecules. They are made up of chains of smaller molecules called amino acids. There are 20 different types of amino acids. 9 of them cannot be produced by the body and can only be obtained through diet. These amino acids are referred to as “essential amino acids”. Ensuring adequate amounts of all amino acids in the body is important to allow the body to maintain tissues and organs and to function.
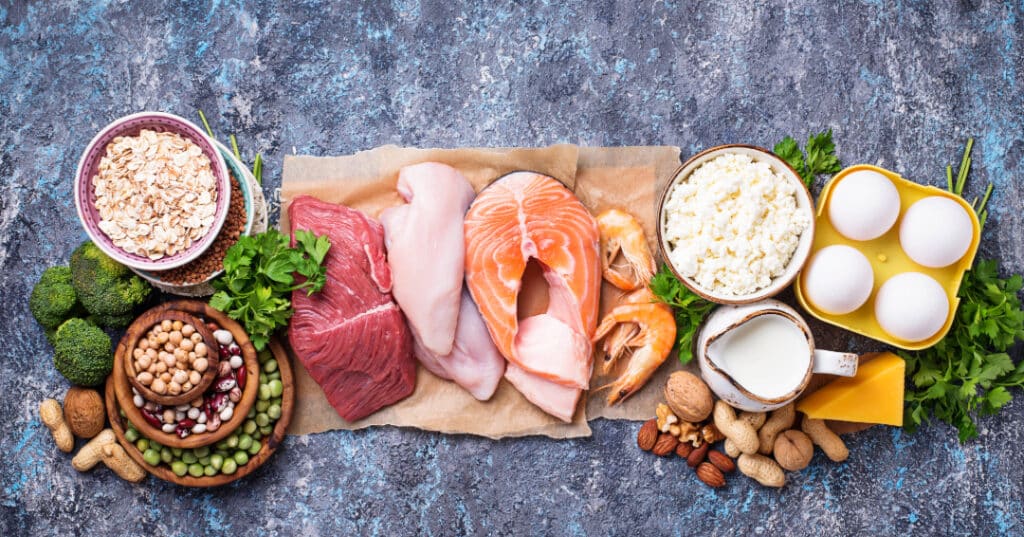
Proteins can be sourced from a variety of foods, both animals and plant-based. Animal sources of protein include meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. Animal-based proteins typically provide all the essential amino acids in adequate amounts, making them complete protein sources. Plant-based sources of protein include legumes, soy products , nuts, seeds, and grains. Individual plant-based sources of protein may lack certain essential amino acids, so ensuring consumption of a combination of a variety of plant-based sources of protein throughout the day is generally recommended.
Proteins are necessary to allow for a wide array of biological functions within the body. Enzymes, which allow for digestion and facilitate other chemical reactions in the body, are largely made up of proteins. Hormones, such as insulin, which regulate a variety of physiological processes within the body, are also made up of proteins. Antibodies, which are vital components of your immune system, are specialised proteins that help defend the body against pathogens. Neurotransmitters, which facilitate communication between nerve cells, are synthesised from certain amino acids found in proteins. The list goes on!
Proteins are also essential for the growth and repair of tissues, including muscles, organs, and connective tissues like tendons and ligaments. Through digestion, proteins are broken down into their constituent amino acids, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream. These are utilised to build and repair tissues, synthesise new enzymes, hormones, antibodies, neurotransmitters, and to carry out various processes essential for life. Each day, up to 300g of protein is consumed and broken down, from which 120-150g is absorbed.


Muscle tissues, are primarily made up of protein. The body will break down muscle tissues when the body finds that it is missing the protein volume necessary to maintain and repair organs and other tissues. This process is known as protein catabolism. This could happen as a result of not meeting your individual dietary protein intake level requirement. Conversely, consuming enough protein through your diet helps to maintain or even increase muscle protein volume. This is particularly important during period of growth, such as childhood and adolescence. It is also important when recovering from injuries or after an intense exercise. As such, ensuring an adequate intake of protein through diet is very important. It allows the body to carry out day-to-day functions, and plays a crucial role in preserving muscle mass, promoting muscle repair and growth.
Growing and development occurs during early childhood and adolescence. Protein requirements are higher to support tissue formation and overall growth.
For an adult, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein typically stands at around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. However, if you are an athlete or are regularly involved in activities that are physically demanding, your protein protein requirement may increase significantly. In such cases, protein needs may range from 1.5 to 1.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day or even more.

Physical activity places additional stress on the muscles, leading to micro-tears that require repair and strengthening. An increased protein intake serves to support muscle repair and growth. Providing the body with an adequate supply of protein allows for muscle recovery. It also increase muscle mass and strength.

As we age, maintaining muscle mass becomes increasingly important. It also becomes more challenging as our bodies become less efficient at both building and preserving it. Maintaining adequate protein intake is important to prevent muscle loss and maintain overall health and functionality in older adults.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein typically remains constant throughout adulthood at around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. Older adults may benefit from slightly higher protein intake to counteract age-related muscle loss.
Adequate protein consumption provides the essential amino acids necessary for muscle protein synthesis, repair, and maintenance. By ensuring a sufficient supply of protein, older adults can potentially mitigate muscle loss. Preserving muscle mass and strength, is necessary to maintain mobility and independence as they age.
For individuals over 60, various factors can make it even more challenging to absorb and maintain protein volume effectively. Older adults may experience decreased efficiency in nutrition absorption in the gut.
This is exacerbated by extended periods of inactivity due to illness or injury which can lead to further muscle loss. Research has shown that two weeks of inactivity may result in 2-3kg losses in muscle mass. This loss of muscle mass not only affects physical strength and function but can also have broader implications for overall health and well-being.

Increasing daily protein intake during periods of inactivity has been demonstrated to mitigate these losses to some extent. By providing the body with a higher supply of amino acids, the building blocks of muscle tissue, individuals may be able to better preserve muscle mass and strength during times of reduced activity or immobility. Therefore, for older adults facing illness, injury, or prolonged periods of inactivity, ensuring adequate protein intake becomes particularly crucial. Incorporating protein-rich foods into their diet and optimizing protein intake is necessary. As it can support muscle health, facilitate recovery, and enhance overall quality of life.
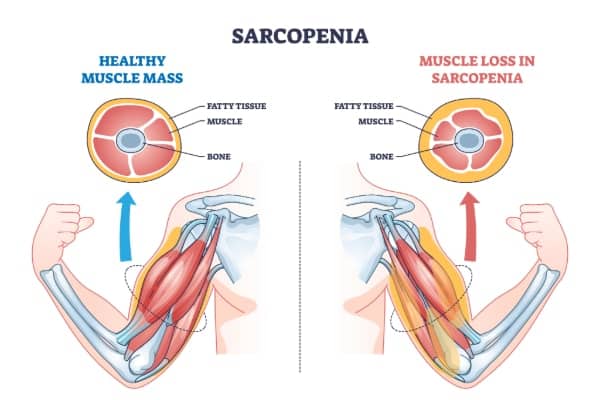
Protein deficiency can have profound consequences on your overall health, affecting various bodily functions and systems.
One of the most notable effects of protein deficiency is muscle wasting. This is where the body breaks down muscle tissue to obtain essential amino acids for vital functions. This can lead to a decrease in muscle mass and strength, impairing mobility, increasing the risk of falls, and impacting overall quality of life, particularly in older adults.
Protein deficiency can also weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Proteins are essential for the production of antibodies. Antibodies play a crucial role in defending your body against pathogens. Without an adequate supply of protein, your body’s ability to mount an effective immune response may be compromised.
Inadequate protein intake can also impede the process of wound healing. This results in prolonged recovery times and increased risk of complications. Proteins are essential for tissue repair and regeneration. Protein deficiency can hinder your body’s ability to heal wounds and injuries effectively.
Sarcopenia, refers to the loss of muscle mass and strength. It is a significant consequence of not maintaining adequate dietary protein intake levels. This is a major concern especially for the aging population. Beyond impacting physical appearance, sarcopenia can have profound consequences on overall health and quality of life.
Decreased muscle mass contributes to a decline in strength and physical performance. This makes everyday tasks more challenging with increasing risk of mobility issues. This can lead to difficulties in maintaining independence and performing activities of daily living. Sarcopenia is also closely associated with an increased risk of falls and fractures. Fall have severe consequences, particularly for older adults. Falls can result in injuries such as fractures, sprains, and head trauma, leading to hospitalization, loss of function, and decreased quality of life.
Loss of muscle mass can also affect metabolic health. Sarcopenia is associated with issues such as insulin resistance and an increased risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes.
Maintaining muscle mass is paramount for overall health and well-being, particularly as individuals age. Muscle plays a vital role in supporting various physiological functions and contributes to overall mobility, strength, and vitality.
Maintaining adequate protein volume within the body is necessary to prevent age-related muscle loss. It is crucial for preserving physical function and independence as individuals grow older. Maintaining muscle mass can be done through regular physical activity and adequate protein intake.

Muscle mass also plays a significant role in metabolic health and disease prevention. Engaging in physical activities and maintaining your muscle mass has several benefits. This includes regulating blood sugar levels, reducing insulin resistance, and lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. Regular exercise itself will not only help with maintaining muscle mass. It will also improve cardiovascular health, enhance immune function, and supports mental well-being. All of which contributes to health promotion.
Prioritizing muscle mass through adequate dietary protein intake in combination with physical activity and fitness is essential for promoting optimal health. Incorporating regular exercise and strength training into daily routines can have far-reaching benefits for long-term health and well-being.
Incorporating high-quality protein sources into your diet is crucial. Foods such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products are excellent sources of complete proteins, providing all essential amino acids in optimal proportions. Plant-based protein sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are also valuable options. However protein absorption from plant-based sources can be less effective. As such, you may need to consume double the quantity of animal-based sources to meet your needs. Plant-based sources of protein also often lack one or more essential amino acids. This necessitates a more varied diet to ensure adequate intake of all essential nutrients.
Some individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet may struggle to obtain enough protein from food sources alone. Protein supplements can be a convenient and effective addition to diet. Whey protein, casein protein, and pea protein shakes are popular choices. They provide a concentrated source of protein that can be easily incorporated into meals or consumed as a snack.
Regular resistance training exercises can stimulate muscle growth and maintenance. Weights, bodyweight exercises, or resistance bands can be used in resistance training. Resistance training promotes muscle protein synthesis and encourage muscle growth. Engaging in a variety of resistance training exercises, targeting different muscle groups and incorporating progressive overload (gradually increasing the resistance or intensity over time), is key to maximizing muscle growth and strength gains. Regular resistance training does not only helps maintain muscle mass. It also offers a range of additional benefits, including improved bone density, enhanced metabolism, better balance and coordination, and reduced risk of injury.
Incorporating resistance training into your fitness routine, alongside a balanced diet rich in high-quality protein, is crucial for supporting muscle health and overall physical performance.
Engaging in regular physical activity during younger years is crucial for building strong muscles and bones. During childhood and adolescence, physical activity plays a vital role in supporting growth and development. This including the accrual of bone mass and the development of muscle strength and endurance. Activities such as running, jumping, and climbing provide the mechanical loading necessary to stimulate bone formation and increase bone density.
Regular exercise during youth also promotes muscle development and strength. Building a solid musculoskeletal foundation allows optimal physical function and mobility in adulthood and beyond. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, help to build lean muscle mass, improve muscle tone, and enhance overall strength and functional capacity.


Staying active in adulthood is essential for maintaining muscle mass and strength. Regular exercise reduces the risk of age-related muscle loss. Typically around their 40s and 50s, individuals may begin to experience a gradual decline in muscle mass and strength. This decline is often exacerbated by factors such as decreased physical activity, hormonal changes, and changes in lifestyle habits.
Regular exercise, particularly resistance training and weight-bearing activities, can help counteract age-related muscle loss. Exercise stimulates muscle protein synthesis and promotes muscle growth and repair. Resistance training exercises are particularly effective at building and maintaining muscle mass and strength.
Building and maintaining muscle mass and strength, enhances overall physical function and reduces the risk of falls in later years by improving stability and mobility. Staying physically active in adulthood is essential for maintaining mobility and supporting overall health and well-being.
Regular exercise is incredibly beneficial for seniors, particularly in improving balance, flexibility, and muscle strength. All of which can significantly reduce the risk of falls and fractures. As you age, you will experience a natural decline in balance and flexibility. This is tied to the gradual loss of muscle mass and strength. These changes can increase the risk of falls and fractures. Falls can have serious consequences for older adults, including injuries, hospitalizations, and loss of independence. Engaging in regular exercise, particularly activities that focus on balance, flexibility, and strength training, can help mitigate these risks.

Balance exercises help improve stability and coordination, reducing the likelihood of falls. Flexibility exercises can help maintain or improve range of motion in the joints, making everyday movements easier and reducing the risk of injury. Strength training, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, are also crucial for older adults. Not only does it help to build and maintain muscle mass and strength, it will also help to maintain bone density. Staying physically active in older adulthood is essential for promoting independence, maintaining mobility, and supporting overall health and well-being. By incorporating regular exercise into their routine, older adults can improve balance, flexibility, and muscle strength, reducing the risk of falls and fractures and enjoying a higher quality of life as they age.
Physical therapy is a valuable resource for older adults seeking to maintain or improve muscle strength and function, as well as overall mobility and quality of life. Physical therapists are highly trained healthcare professionals who specialize in assessing and treating movement impairments and musculoskeletal conditions. They work closely with older adults to develop individualized exercise programs tailored to their specific needs and goals.
Through targeted exercises and mobility training, physical therapy can help older adults:
1. Improve Muscle Strength: Physical therapists prescribe exercises that target specific muscle groups to improve strength and endurance. These exercises may involve using resistance bands, free weights, or bodyweight exercises to gradually increase muscle strength over time.
2. Enhance Balance and Coordination: Balance exercises are an essential component of physical therapy for older adults. These exercises focus on improving stability and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and enhancing overall mobility.
3. Increase Flexibility and Range of Motion: Stretching exercises help improve flexibility and range of motion in the joints, making it easier for older adults to perform daily activities and maintain independence.
4. Manage Pain and Improve Function: Physical therapists may use a variety of techniques, such as manual therapy, therapeutic modalities, and ergonomic education, to help manage pain and improve functional mobility.
5. Promote Safe and Effective Movement: Physical therapists educate older adults on proper body mechanics and techniques to prevent injury and promote safe and effective movement during daily activities.
Overall, physical therapy plays a crucial role in helping older adults maintain and improve muscle strength and function, preserve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life. By working closely with a physical therapist, older adults can receive personalized care and support to achieve their health and wellness goals.
Protein is essential for maintaining muscle health throughout life, and combining an adequate protein intake with regular physical activity supports muscle growth and maintenance, leading to a healthier and more active lifestyle. Proteins provide the necessary building blocks for muscle repair and growth, found in sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and nuts. Engaging in activities such as strength training and resistance exercises stimulates muscle protein synthesis, enhancing muscle strength and function. Prioritizing protein intake and physical activity not only promotes muscle health but also offers additional benefits like improved metabolism, balance, and bone density, making it vital for overall well-being at every stage of life.
Forest Lodge, Annandale, Glebe, Leichhardt, Balmain, Haberfield, Canada Bay, Rozelle, Rodd Point, Wareemba, Stanmore, Petersham, Lilyfield, Hunters Hill, Enfield, Cabarita, Mortlake, Rhodes, Burwood Heights, Birchgrove, Gladesville, Huntleys Point, Abbotsford, Ashfield, Croydon Park, Croydon, Chiswick, Russell Lea, Burwood, Strathfield, Concord, Drummoyne, North Strathfield, Liberty Grove, Dulwich Hill, Lewisham, Camperdown, Ashbury, Homebush, Homebush West, Woolwich, Henley, Summer Hill, Sydney Olympic Park
212 Great North Road, Five Dock, NSW 2046
Onsite parking available
Phone: 02 9712 1736
Email: [email protected]

About
Five Dock Osteopathic & Chiropractic is located in Canada Bay, in Sydney’s Inner West. Servicing suburbs including Burwood, Croydon, Drummoyne, Five Dock, Haberfield, Concord, Abbotsford, Chiswick, Leichhardt, Wareemba, Russell Lea, Summer Hill, Strathfield.
Clinic hours
Monday, Tuesday, Thursday 7AM – 7PM
Wednesday, Friday 7AM – 6PM
Saturday 7AM – 2PM
Sunday 8AM – 2PM
Contact details